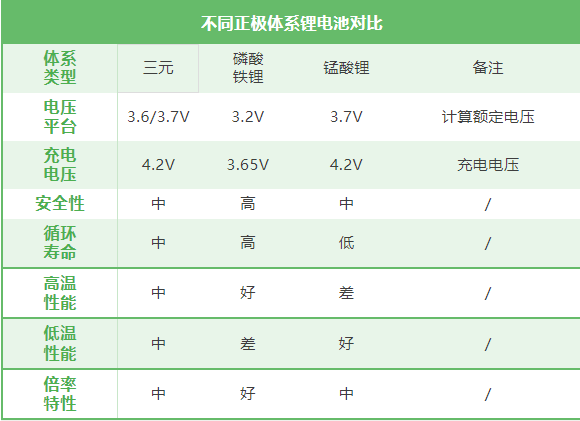
In order to calculate the voltage and capacity of lithium batteries, we must first understand the voltage of different cathode materials to calculate the rated voltage.
ONE. Voltage calculation
1, single cell voltage: different types of lithium battery single cell rated voltage is different. For example, the rated voltage of ternary lithium batteries is generally 3.6V or 3.7V (the voltage after full charge is usually 4.2V); The rated voltage of the lithium iron phosphate battery is 3.2V (the voltage after full charge is about 3.65V). This is a fixed voltage parameter that can be directly determined according to the cell type.
2, battery pack voltage (series case) : when multiple cells are connected in series, the total voltage of the battery pack is equal to the sum of the voltages of each cell. For example, 10 ternary lithium cells with a rated voltage of 3.6V are connected in series, and the battery pack voltage is 3.6V×10 = 36V; The 15 lithium iron phosphate cells with a rated voltage of 3.2V are connected in series, and the battery pack voltage is 3.2V×15 = 48V.
3, battery pack voltage (parallel case) : multiple cells in parallel, the voltage is unchanged, and the voltage of a single cell is the same. For example, no matter how many 3.7V ternary lithium battery cells are in parallel, the voltage of the battery pack is always 3.7V.
TWO. Capacity calculation
1, single cell capacity: the capacity of the cell is usually in ampere-hours (Ah) or milliampere-hours (mAh) as a unit, indicating the amount of electricity that the battery can provide under certain discharge conditions. For example, a cell with a capacity of 2600mAh means that the cell can discharge continuously for 1 hour at a current of 2600mah under certain discharge conditions.
2, battery pack capacity (in series) : in series, the capacity of the battery pack is the same as that of a single cell. Because the series only increases the voltage, and the current path does not change, the capacity does not change.
3, battery pack capacity (parallel case) : in parallel, the capacity of the battery pack is equal to the sum of the capacity of each cell. For example, 10 ternary lithium cells with a capacity of 2600mAh are connected in parallel, and the battery pack capacity is 2600mAh×10 = 26000mAh.
THREE, determine the number of strings and several
1, determine the number of series: according to the total voltage of the battery pack required and the rated voltage of the single cell to determine the number of cells in series. The formula is: series number = total battery voltage ÷ rated voltage of single cell. For example, to assemble a 48V ternary lithium battery pack, the rated voltage of the ternary lithium battery is 3.7V, then the series number = 48 ÷ 3.7 ≈ 13 (generally integer and need to be adjusted according to the actual situation, may take 13 strings or 14 strings, 13 strings when the charging voltage is 54.6V, The charging voltage is 58.8V at 14 series); If a 48V lithium iron phosphate battery pack is assembled, and the rated voltage of the lithium iron phosphate battery is 3.2V, the number of series = 48 ÷ 3.2 = 15 strings.
2, determine the number of parallel: according to the total capacity of the battery pack and the capacity of the single cell to determine the number of parallel cells. The formula is: parallel number = total battery capacity ÷ single cell capacity. For example, to assemble a 48V, 20Ah ternary lithium battery pack, use a single 18650 cell with a capacity of 2Ah, first determine the series number of 48 ÷ 3.7 ≈ 13 series according to the voltage, and then determine the parallel number = 20Ah ÷ 2Ah = 10 according to the capacity, So the total number of cells required is 13×10 = 130 cells.